Imagine the leaders that inspire you. Each is likely unique, with a different style they use to meet goals, motivate, and animate their teams. There are many different styles of leadership, and each can have a different impact on a company.
In this post, we’ll cover the most common types of leadership, how they influence business, and give tools to help you figure out what styles are best for you.
Start reading, or jump to the section you’re looking for:
What is a leadership style?
A leadership style refers to a leader’s methods and behaviors when directing, motivating, and managing others. A person’s leadership style also determines how they strategize and implement plans while accounting for the expectations of stakeholders and the well-being of their team.
Why It’s Important to Know Your Leadership Style
Knowing your leadership style helps you provide adequate guidance and feedback to employees, and better understand your thoughts, how you make decisions and strategies you can consider implementing when making business decisions.
It can also help you understand how your direct reports see you and why they may give you specific feedback. For example, if employees feel stifled at work and don’t have many opportunities to speak their minds, they may be telling you that you’re an autocratic leader who can benefit from changing their style.
Knowing your leadership styles may help you improve with limited feedback. Each leadership style has its pitfalls, allowing you to proactively address areas of improvement. This is critical because some employees might hesitate to speak up, even in an anonymous survey.
Ready to find out your leadership styles? Check out the most common styles below.
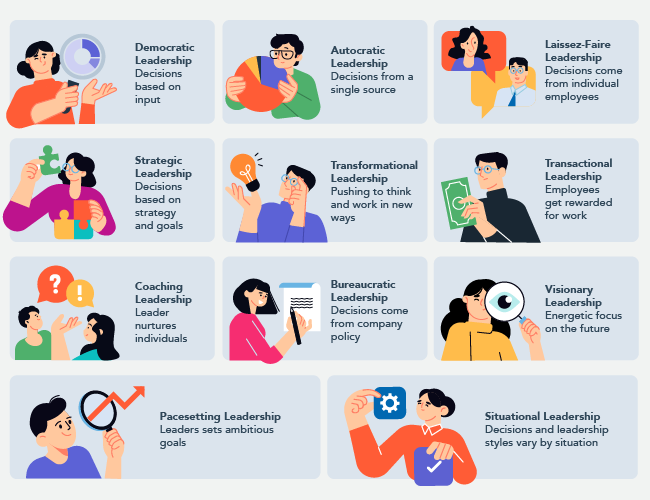
Types of Leadership Styles
- Democratic Leadership
- Autocratic Leadership
- Laissez-Faire Leadership
- Strategic Leadership
- Transformational Leadership
- Transactional Leadership
- Coaching Leadership
- Bureaucratic Leadership
- Visionary Leadership
- Pacesetting Leadership
- Situational Leadership
1. Democratic Leadership
Also called: Participative or Facilitative Leadership
Democratic leadership is exactly what it sounds like — the leader makes decisions based on each team member‘s input. Although a leader makes the final call, each employee has an equal say in a project’s direction.
Democratic leaders often have the following characteristics:
- Inclusive
- Collaborative
- Effective communicator
- Empowering
- Supportive and empathetic
- Trust-building
- Emotionally intelligent
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
This leadership style resembles how leaders often make decisions in company board meetings.
For example, a democratic leader might give the team a few decision-related options in a company board meeting. They could then open a discussion about each option. After a discussion, this leader might consider the board’s thoughts and feedback, or they might open this decision up to a vote.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
The democratic leadership style is one of the most effective because it encourages everyone to participate in all processes, share their opinions, and know that you will hear them. It also encourages employees to be engaged because they know you will hear their feedback.
Team members feeling like they have space to participate can also increase employee empowerment, motivation, and participation.
Potential challenges for leaders with a Democratic style:
Reaching a consensus can take considerable time, resources, and communication with a democratic style. It can also impact decision-making because some team members may not have the right expertise to make critical decisions.
Featured resources:
2. Autocratic Leadership
Also called: Authoritarian, Coercive, or Commanding Leadership
Autocratic leadership is the inverse of democratic leadership. In this leadership style, the leader makes decisions without taking input from anyone who reports to them.
Autocratic leadership is typically characterized by:
- Centralized decision-making
- Direct and top-down communication
- Minimal delegation
- Limited autonomy for team members
- Emphasis on hierarchy and status
- Resistant to feedback or criticism
This style is most useful when a business needs to control specific situations, not as a standalone leadership style. For instance, it can be effective in emergency or crisis situations where quick and decisive action is necessary.
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
Autocratic leaders carry out strategies and directives with absolute focus. So, when a situation calls for it, an authoritative leader can make a quick best-fit decision for a business without needing to get additional input (helpful on a case-by-case basis).
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
This type of leadership is most effective when a company makes difficult decisions that don’t benefit from additional input from others who aren’t fully knowledgeable on the subject. Responsible parties can make a decision and give employees a clear sense of direction, and it can also make up for a lack of experience on a team.
Potential challenges for leaders with an Autocratic style:
Most organizations can’t sustain such a hegemonic culture without losing employees, which can significantly lower morale and creative problem-solving.
An example of authoritative leadership gone bad could be when a manager changes the hours of work shifts for employees without consulting anyone.
Other challenges with autocratic leaders include:
- Intimidation
- Micromanagement
- Over-reliance on a single leader
3. Laissez-Faire Leadership
Also called: Delegative or Hands-off Leadership
If you remember your high-school French, you’ll accurately assume that laissez-faire leadership is the least intrusive form of leadership. The French term “laissez-faire” literally translates to “let them do.”
Leaders who embrace it give nearly all authority to their employees and don’t often interject unless the situation calls for it.
Some key characteristics of laissez-faire leadership include:
- Limited guidance, direction, and feedback
- Minimal interference and control
- High autonomy and freedom
- Empowerment and trust
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
Laissez-faire leaders make employees accountable for their work. This gives many employees an incentive to do their best work.
This type of leader often creates a more relaxed company culture. This makes it a good model for creative businesses like ad agencies or product design. It’s also a good fit for a business with a highly-skilled team.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
In a young startup, for example, you might see a laissez-faire company founder who makes no major office policies around work hours or deadlines.They might put complete trust in their employees while they focus on the overall workings of running the company.
Because of this high level of trust, employees working for laissez-faire leaders feel valued. They get the information they need and use their resources and experience to meet business goals.
Potential challenges for leaders with a Laissez-Faire style:
Although laissez-faire leadership can empower employees by trusting them to work however they’d like, there are downsides. It can limit team development and pose a challenge for new or inexperienced employees who would benefit from guidance as they get ramped up. Roles and responsibilities can also become unclear, and it can build a culture of working in silos where people might work autonomously rather than as a cohesive group.
This style can lead to overlooking critical company growth and learning opportunities, so keeping this leadership style in check is important.
Featured resources:
4. Strategic Leadership
Strategic leaders sit between a company’s primary operations and its growth opportunities. This form of leadership requires vision, competitive awareness, and adaptability.
These leaders accept the burden of executive interests but also ensure that working conditions are stable for everyone else.
Strategic leaders aim to guide their organization toward its long-term goals. By utilizing this leadership style, you can create a forward-thinking, agile, and adaptable organization that can thrive in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
Strategic leaders tie plans for growth and strategy to how they manage a team. They ask questions, develop and execute strategies, and consider future growth. This approach supports popular business goals like:
- Accountability
- Productivity
- Collaboration
- Transparency
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
This is a desirable leadership style in many companies because strategic thinking supports many types of employees at once.
Strategic thinking supports many employees at once, so it’s a desirable style for many companies. It encourages visualization, planning, and making the most of existing resources, and it can motivate employees.
Potential challenges for leaders with a strategic leadership style:
Leaders who work strategically might take on too much and risk thinking too far into the future of possibilities while missing critical present-day issues. It’s important to learn how to delegate with this leadership style and share the weight of decision-making.
Compromise, communication skills, and consistent outreach are also essential.
Featured resources:
5. Transformational Leadership
Transformational leaders gain the trust and confidence of their teams, encourage team members, and lead employees toward meeting company goals.
Transformational leadership also always improves upon the company’s conventions and motivates employees to grow and further develop their skills.
Ultimately, the goal of a transformational leader is to create a lasting positive impact, uplift their team to achieve their full potential, and drive success for the organization.
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
Transformational leaders can inspire their teams to think in new ways. This can help companies update business processes to improve productivity and profitability. It can also help with employee satisfaction, morale, and motivation.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
This is a highly encouraging form of leadership where employees are supported and encouraged to see what they’re capable of.
When starting a job with this type of leader, all employees might get a list of goals to reach and deadlines for reaching them. The goals might begin quite simple, but as employees grow and meet their goals, leaders will give them more tasks and challenges to conquer as they grow with the company.
Potential challenges for leaders with a Transformational style:
Transformational leaders can lose sight of everyone’s individual learning curves in place of the company’s goals. Employee burnout can also become an issue, so it’s important to work with your team to update benchmarks.
Featured resources:
6. Transactional Leadership
Transactional leadership is based on reward and punishment to motivate and direct the behavior. These managers set specific rules and standards, and they closely monitor their employees’ performance. They tell employees they can expect rewards if a goal is met. However, they may require more 1:1s or check-ins if people aren’t meeting goals.
This leadership style is concerned with maintaining the status quo and ensuring that predetermined goals and standards are met. It also assumes that teams need structure and monitoring to meet business goals and that they are reward-motivated.
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
This style is popular in enterprise companies as it focuses on results, existing structures, and set systems of rewards or penalties. This leadership style also recognizes and rewards commitment.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
Transactional leaders can offer helpful clarity and structure of expectations, which can help employees feel safe because they understand expectations. Employees also have a clear view of what they get in return for meeting business goals.
Potential challenges for leaders with a transactional style:
This style is more about using rewards to motivate and less about building relationships with employees, coaching, and developing team morale. Keeping a diverse team engaged can be hard if only some are reward-motivated, and it can lead to low creativity and fear of punishment.
7. Coaching Leadership
Also called: Conscious Leadership
A coaching leader focuses on identifying and nurturing the individual strengths of each member of the team and developing strategies that will enable teams to work better together.
This style is similar to strategic and democratic leadership, but it emphasizes individual employees’ success.
A manager with this leadership style might help employees improve on their strengths by:
- Giving them new tasks to try
- Offering guidance
- Meeting to discuss constructive feedback
They might also encourage one or more team members to expand on their strengths by learning new skills from other teammates.
Coaching leaders focus on building trust and establishing strong relationships with their team members. They foster an environment of open communication and psychological safety that encourages individuals to share ideas, seek feedback, and work together toward common objectives.
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
Coaching leaders actively support skill development and independent problem-solving. They meet ambitious business goals by creating a strong company culture and add to a business’s long-term vision as valuable mentors, often even after leaving a company.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
This leadership style can motivate employees as they feel supported on the team. It recognizes that each employee is unique and can build diverse and exciting teams where each employee offers something different.
This leader focuses on high performance, with employees that can communicate well and embrace unique skill sets to get work done. They also encourage team members to seek new challenges, learn from experiences, and continuously improve their skills and knowledge.
Potential challenges for leaders with a coaching style:
It can take a lot of time to develop employees with a coaching style, but mentoring isn’t effective for every employee.
Featured resources:
8. Bureaucratic Leadership
Bureaucratic leaders follow the rules. Unlike autocratic leadership, they might listen and consider the input of employees, but they might reject input that doesn’t align with company policy or past practices.
Some key features of bureaucratic leadership include:
- Centralized decision-making
- Strict adherence to rules and procedures
- Clear chain of command
- Limited autonomy
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
This style works best for larger, older, or traditional companies that are successful in their current processes. This leadership style works for these businesses because they want to maintain existing business models and processes because their current strategies are successful, and trying something new that doesn’t work could waste time and resources.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
This leadership style can be challenging for some, but it has many benefits. It lowers the risk of favoritism and replaces it with central duties, job security, and predictability.
This clear and efficient leadership style can lead to high levels of creativity for some employees.
Potential challenges for leaders with a bureaucratic leadership style:
Employees might not feel as controlled as autocratic leadership, but there can be a lack of freedom in how much people can do in their roles. This approach can shut down innovation and is not the right fit for companies chasing ambitious goals and quick growth.
Featured resources:
9. Visionary Leadership
Also called: Affiliative Leadership
Visionary leadership focuses on future and long-term goals. They aim to inspire and guide their team towards the achievement of a shared vision.
This type of leader encourages collaboration, emotional intelligence, and teamwork. They also foster a culture of innovation and change, encouraging individuals to embrace new ideas and approaches.
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
Visionary leaders can create a clear plan for employees to follow and execute. They are powerful and persuasive communicators, which helps them energize teams toward impactful business growth.
As the focus is on future growth, visionary leaders can forecast potential roadblocks and outline action plans, giving employees increased confidence during uncertainty or challenging times.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
Teams can do more and enjoy their work more if they have a vision to work toward. This type of leader offers vision statements and other tools to inspire and motivate teams to engage at work.
Potential challenges for leaders with a visionary style:
Visionary leaders can skip over day-to-day issues to focus on long-term ideas, missing roadblocks that could build up and cause problems in the future. Another common challenge is hyper-focus on a single goal, which can impact consideration for other ideas that may be just as valuable to the business.
Featured resources:
10. Pacesetting Leadership
A pacesetting leader sets ambitious standards and expects employees to meet those goals in the exact manner they’ve laid out. These leaders expect productivity and high-quality outputs from employees, and they may step in to ensure things are done correctly and on time.
Some characteristics of a pacesetting leader include:
- High performance standards
- Leading by example
- Results-oriented
- Preference for speed and efficiency
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
This type of leader sets ambitious goals with a clear and focused effort, so employees know exactly what is expected of them. For example, pacesetting sales leaders set and exceed ambitious quarterly sales cadences.
These leaders might also work alongside their team and push performance, boosting team morale.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
Skilled and experienced teams often thrive under this kind of leader. They use the abilities of motivated and competent team members and make meeting goals feel urgent and exciting.
It can also be gratifying for team members to see their leader working hard alongside them.
Potential challenges for leaders with a pacesetting style:
Pacesetting leaders can sometimes create a high-stress workplace environment if goals are unrealistic, which can overwhelm and demotivate teams. This can impact engagement and lead to burnout, where people struggle to meet goals and perform as expected.
Focusing on goals can also stifle creativity and diversity of thought, so employees don’t feel they can use their expertise to suggest alternative goals or strategies.
Featured resources:
11. Situational Leadership
Situational leaders change their management style to meet the needs of the situation or team. It suggests that effective leaders must adapt their leadership style to match the readiness and development levels of their team members
This leadership style involves analyzing specific situations, assessing the competence and commitment of individuals, and adjusting the leadership approach accordingly. It is proactive and recognizes that change is the only constant.
Why this leadership style works for businesses:
This leadership approach can motivate employees and ensure that people aren’t stuck working in a way that doesn’t make sense for the situation. It’s also valuable for startups or businesses requiring frequent changes and flexible talent and support.
Why this leadership style is good for the team:
Situational leaders are great communicators and use team feedback to make decisions. They also analyze market changes and can quickly evaluate and update processes to ensure success. This can create strong relationships and help employees see and feel their value to the business.
Potential challenges for leaders with a situational style:
Leaders need a high level of expertise in all business processes and functions to make decisions, and they must be able to pivot quickly. It’s important to remember long-term goals and meet immediate needs; not every leader can do this effectively.
It can become confusing and stressful for teams if a leader’s approach changes too often, as they won’t know what to expect.
Featured resources:
Deciding Between Different Leadership Styles
There’s no single “best” leadership style, so figuring out what is best for you and your environment is essential.
How to Understand Your Instinctive Leadership Style
Leaders need good instincts, and many leaders focus on their own experiences and habits as they develop a leadership style. As you start your path toward leadership, you may want to keep notes. Write down how you would handle specific situations or problems.
Doing this can help you be a confident and capable leader, but if you notice things aren’t going as expected, you may want to reconsider your approach.
Your instincts and habits will always impact the way you lead. But if you find yourself in situations that you’re unsure how to respond to, you may want to look at other leadership styles.
For example, if you’re an extrovert with a shy member on your team, you may want to work on active listening. If you’re an introvert leading a team of outgoing people, you may need to learn new ways to nurture, support, and inspire your team.
Can you change your leadership style?
While it may take some time and effort, you can always change your leadership style and improve your processes.
The first step to making changes is recognizing the need for change. Whether this comes from direct employee feedback, noticing that goals aren’t being met, or people seeming to experience burnout, identifying this is the first step.
Next, you need to prepare yourself for changes. For example, your leadership style may be effective for your team, but you might have a more challenging time connecting with stakeholders. In this case, you wouldn’t want to throw out your current style, but you’d want to identify what is and isn’t working. Then, get curious, and begin the work of adjusting the way you lead.
How to Choose the Right Leadership Style for You
There are many ways to find a leadership style that works for you. Because of this, it can be tough to know where to begin. If you’re not sure what leadership styles will work for you, these steps can help.

1. Get to know yourself.
Everyone has a unique path to self-discover. Some take risks and try new things and others prioritize quiet time, writing exercises, and listing strengths and weaknesses.
Another path to learning about yourself is through physical activity and spending time with other people. However you go about it, getting to know yourself is an important first step toward being a leader.
2. Outline your values and challenges.
Knowing yourself will help you understand what’s important to you and where you struggle. Being a leader means working quickly and making decisions quickly, so having your values mapped out can be extremely helpful.
As you write out your values, look at pivotal moments in your life to date. Then, look for trends, people you’re drawn to, and common themes. If your list is long, group similar ideas together.
Having an outline can help you see how you react, your strengths and weaknesses, and a base for your core values.
3. Watch leaders you respect.
Observing leaders you respect can also help you define your leadership style. As you watch them in meetings, client conversations, and presentations, take notes of what you like.
Another approach is to view their actions with specific leadership styles in mind, helping you figure out what their approach is and whether it will work for you.
4. Try different leadership styles.
A hands-on option is to try out different leadership styles. You can create an outline of what interests you and review your notes before your next meeting to see how you can incorporate it into your interactions.
5. Find a business coach or mentor.
Working with a business coach can also help you hone your leadership style.
A mentor can be someone in your workplace you respect and would appreciate feedback from, whether it’s another leader or a colleague you respect. You can also check out this guide on how to find a business coach.
6. Ask colleagues and leaders for feedback.
Another way to find the best style for your needs is to ask other colleagues, leaders, and team members for feedback.
The best approach for this strategy is to plan out what you want to ask and why so you get the feedback you need. Think about how people might respond and also set clear guidelines and expectations.
When you get feedback, make sure to listen carefully. You’ll gain valuable information about your strengths and weaknesses that will help you understand where you need to improve and the style that will help you improve.
7. Complete a leadership style assessment.
Leadership assessments are helpful tools for leaders, for yourself as an individual, and to assess your teams.
A leadership quiz can make it easier to understand your strengths and skills. It can surface habits and qualities you might not be aware of and give you a clear direction for growth.
If this is something you want to try, the leadership assessment below is a great place to start.
Leadership Style Assessment
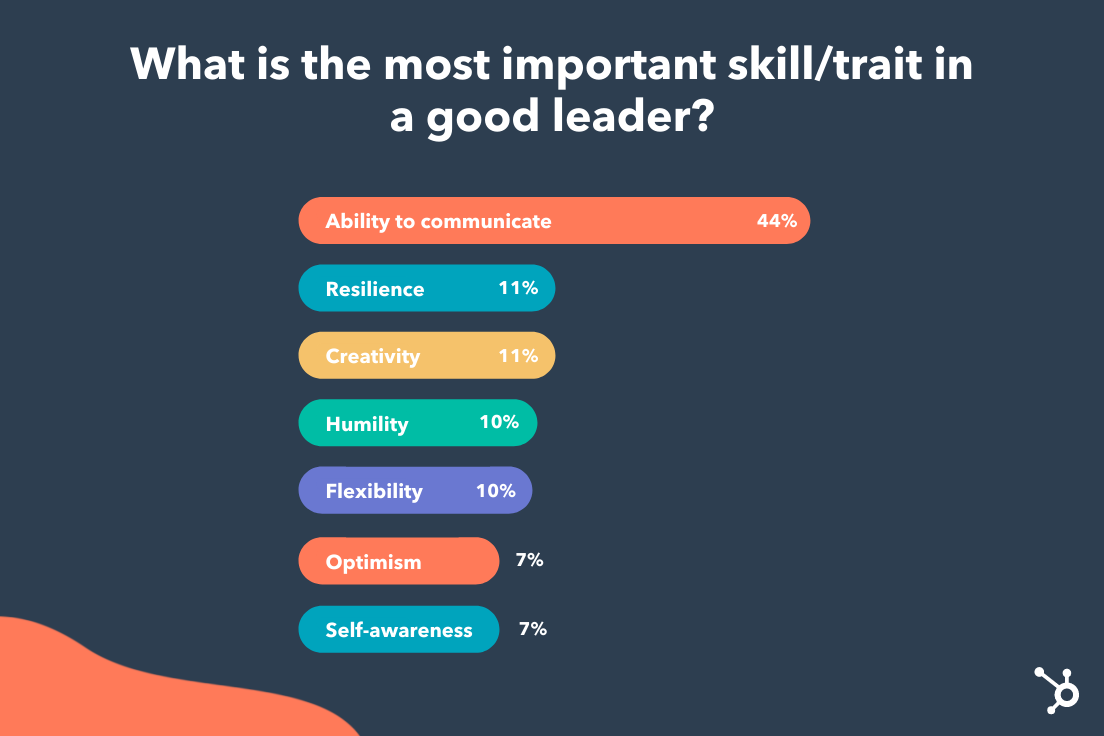
Leaders carry a mix of the leadership styles mentioned above. At the root of these styles, leadership experts Bill Torbert and David Rooke say, are what are called “action logics.”
These action logics assess “how [leaders] interpret their surroundings and react when their power or safety is challenged.”
That’s the idea behind the Leadership Development Profile, a popular management survey tool. Created by professor Torbert and psychologist Susanne Cook-Greuter — and featured in the book, Personal and Organizational Transformations — the survey uses a set of 36 open-ended sentence completion tasks to help researchers better understand how leaders develop and grow.
Below we’ve used open-ended sentences to outline six action logics that describe each one. Review the sentences, see how they resonate with you, and figure out which leadership style upholds based on the action logic you most align with.
1. Individualist
The individualist is self-aware, creative, and primarily focused on their actions and development as opposed to overall organizational performance. This action logic is exceptionally driven by the desire to exceed personal goals and constantly improve their skills.
Here are some things an individualist might say:
Individualist 1: “A good leader should always trust their own intuition over established organizational processes.”
Individualist 2: “It’s important to be able to relate to others so I can easily communicate complex ideas to them.”
Individualist 3: “I’m more comfortable with progress than sustained success.”
2. Strategist
Strategists are acutely aware of the environments they’re in and have a deep understanding of the structures and processes that make their businesses tick. Still, they’re also able to evaluate what could be improved.
Here are some things a strategist might say:
Strategist 1: “A good leader should always be able to build a consensus in divided groups.”
Strategist 2: “It’s important to help develop the organization as a whole, as well as the growth and individual achievements of my direct reports.”
Strategist 3: “Conflict is inevitable, but I’m knowledgeable enough about my team’s personal and professional relationships to handle the friction.”
3. Alchemist
Rooke and Tolbert describe the alchemist as highly evolved and effective at managing organizational change. They differ from other action logics in their unique ability to simultaneously see the big picture and minute details. No department or employee gets overlooked with an alchemist leader.
Here are some things an alchemist might say:
Alchemist 1: “A good leader helps their employees reach their highest potential, and possesses the necessary empathy and moral awareness to get there.”
Alchemist 2: “It’s important to make a profound and positive impact on whatever I’m working on.”
Alchemist 3: “I have a unique ability to balance short-term needs and long-term goals.”
4. Opportunist
Opportunists are guided by a certain level of mistrust of others, relying on a facade of control to keep their employees in line. “Opportunists tend to regard their bad behavior as legitimate in the cut and thrust of an eye-for-an-eye world,” Rooke and Tolbert write.
Here are some things an opportunist might say:
Opportunist 1: “A good leader should always view others as potential competition to be bested, even if it’s at the expense of their professional development.”
Opportunist 2: “I reserve the right to reject the input of those who question or criticize my ideas.”
5. Diplomat
Unlike the opportunist, the diplomat isn’t concerned with competition or assuming control over situations. Instead, this action logic seeks to cause minimal impact on their organization by conforming to existing norms and completing their daily tasks with as little friction as possible.
Here are some things a diplomat might say:
Diplomat 1: “A good leader should always resist change since it risks causing instability among their direct reports.”
Diplomat 2: “It’s important to provide the ‘social glue’ in team situations, safely away from conflict.”
Diplomat 3: “I tend to thrive in more team-oriented or supporting leadership roles.”
6. Expert
The expert is a pro in their given field, constantly striving to perfect their knowledge of a subject and perform to meet their own high expectations. Rooke and Tolbert describe the expert as a talented individual contributor and a source of knowledge for the team. But this action logic does lack something central to many good leaders: emotional intelligence.
Here are some things a diplomat might say:
Expert 1: “A good leader should prioritize their own pursuit of knowledge over the needs of the organization and their direct reports.”
Expert 2: “When problem-solving with others in the company, my opinion tends to be the correct one.”
Which Leader Are You?
So, which action logics above felt like you? Think about each sentence for a moment.
Now, check out which of the seven leadership styles you embrace on the right based on the sentences you resonated with on the left.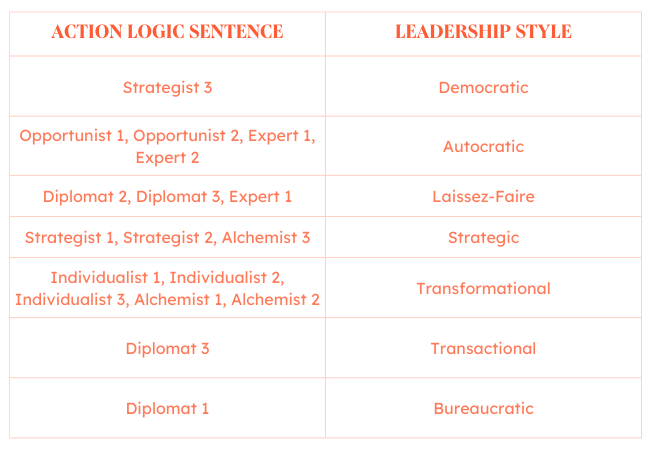
The more action logics you agree with, the more likely you are to practice a mix of leadership styles.
For example, if you agreed with everything the strategist said, this would make you a 66% strategic leader and 33% democratic leader. If you agreed with the third statement and everything the alchemist said, this would make you a 50% transformational, 25% strategic, and 25% democratic leader.
Keep in mind that these action logics are considered developmental stages, not fixed attributes — most leaders will progress through multiple types of leadership throughout their careers.
Learn Your Leadership Management Style to Become a Better Leader
Whether you manage a big or small team, your leadership style heavily impacts how your direct reports see you and how your team works together to achieve your company’s goals. There are many different styles of leadership, so choosing one that works for you can make you a more effective leader.
If you want to be a leader that makes a difference, you’ll need to keep growing and embrace change. Are you ready to get started?
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in August 2016 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

![→ Click here to download leadership lessons from HubSpot founder, Dharmesh Shah [Free Guide].](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/4e634041-e1ce-4a85-8e65-aea12fc10b84.png)

![The 11 Most Common & How to Find Your Style [Quiz]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/product-life-cycle_0.webp#keepProtocol)
![The 11 Most Common & How to Find Your Style [Quiz]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/Chrome%20Extensions%20(1).png#keepProtocol)
![How to Optimize for Google’s Featured Snippets [Updated for 2024]](https://moz.com/images/blog/Blog-OG-images/How-to-Optimize-for-Googles-Featured-Snippets-OG-Image.png?w=1200&h=630&q=82&auto=format&fit=crop&dm=1724004002&s=13df73104762982790dab6dc8328023f)


