Whether you’re an entrepreneur looking for investors for your small business or the CEO of a large corporation, an executive summary can help you succeed and is a critical component for long-term growth.
A short, attention-grabbing executive summary is an essential part of your business plan. Done correctly, it will ensure your company becomes or remains a key player in your industry. In this post, you’ll learn what an executive summary is and how to write one that engages investors, customers, and general audiences.
Executive Summary
An executive summary is a brief overview of a long document, such as a business plan, proposal, or report. It’s a section that grabs readers’ attention and summarizes critical information from the document, such as the problem or opportunity being addressed, objectives, key findings, goals, and recommendations.
Some documents that may have an executive summary include:
- Business plans
- Research documents
- Project proposals
- Annual reports
Ultimately, the executive summary is meant to inform readers of the most important information in the document, so they don’t have to read it all and can get caught up quickly.
Executive Summary vs. Business Plan
All business plans have an executive summary, but not all executive summaries belong to business plans.
A business plan includes a company overview, your company’s short-term and long-term goals, information on your product or service, sales targets, expense budgets, your marketing plan, and a list including each member of your management team. In this case, the executive summary is the first section of the business plan that convinces readers that it’s worth their time to read the whole thing.
Business plans are very detailed and comprehensive, and can be as short as a dozen pages or as long as 100 pages. However, a CEO or investor might not have the interest or time to read your full business plan without first getting the general gist of your company or goals through an executive summary.
Executive Summary vs. Mission Statement
Mission statements and executive summaries are typically both found in business plans, but they serve different purposes.
A mission statement defines your organization’s purpose, values, and vision. It’s your company’s north star and communicates your core identity and reason for existence. On the other hand, an executive summary provides a high-level overview of the document.
Ultimately, your mission statement provides direction for developing your business plan, while your executive summary describes your business plan to executives and shareholders.
Executive Summary vs. Company Description
Like mission statements and executive summaries, company descriptions can also be found in business plans as well as the “About us” page of your website. It provides an overview of your business, including essential details like company history, what your company does, unique selling points, goals, management team, and overall value proposition.
Executive Summary vs. Objective
An objective is a specific goal or target that your company takes aims to achieve its overall goal. It is a concrete, measurable outcome that guides your business’s actions and decisions. Objectives are usually set at the strategic level and are typically aligned with the company’s mission, vision, and overall strategic plan.
Company objectives are often included in executive summaries, but are not the sole focus of them.
What is the purpose of an executive summary?
Writing an executive summary may not seem that necessary. After all, you can find the same information just by reading the rest of the document.
However, the executive summary serves many purposes for your document and those who read it. Here are some of the benefits of having one:
- It saves your readers time. CEOs and investors often have limited time to review lengthy documents. An executive summary allows them to quickly grasp the main points, key findings, and recommendations without needing to read the entire document.
- It provides clarity and conciseness. By providing a condensed overview, executive summaries help to distill complex information and present it in a manner that’s easy to understand.
- It helps with document navigation. For longer documents or reports, an executive summary provides a roadmap for readers. It helps them navigate through the document by signaling the main sections or topics covered, improving overall document usability and accessibility.
To write an impressive executive summary that effectively embodies all the important elements of your business plan, we’ve cultivated a list of necessary components for an executive summary, as well as an example to get you started.
Follow Along With HubSpot’s Executive Summary Template
Click to Download
How to Write an Executive Summary
A good executive summary tells your company’s story, contains in-depth research, conveys information with an appropriate tone, is void of clichés, and follows your business plan’s structure. These elements will ensure your executive summary is effective, informative, and impactful.
1. Tell your story.
When investors or CEO’s read your executive summary, they should understand what your business is about. This is one of the first elements of your business plan, so it should set the tone.
In your executive summary, be sure to tell your story and include an overview about what your company does and why you do what you do. You can also briefly highlight important details about your company’s management.
For instance, you could talk about your founder or CEO’s qualifications and motivations. You can also provide a high-level summary of your company’s business operations and any management methods or best practices that you abide by.
You’ll also want to explain the problem or opportunity that is being addressed, and how it is valuable to investors and customers. Think of this like an elevator pitch. If someone stopped reading and you only had the executive summary to explain your company, what information would you include?
2. Highlight important data.
An executive summary, while short, should include plenty of research.
Highlight the most important findings and insights from the document, including any critical data or statistics discovered in your competitor analysis. While your business plan will flesh out the details, it’s important to include your key findings in your executive summary.
You should also provide a basic rundown of your target market, how you plan on addressing their needs and pain points, and how you will reach them.
Additionally, you should include key financial information. The main points you should cover are the overall budget, the price per product/service, and your financial projections.
3. Pay attention to your tone.
Although the tone of your executive summary should be professional and concise, it should also be true to your company and target audience. Aim to convey a sense of authority and credibility while remaining accessible and engaging.
Here are some tips to keep in mind:
- Focus on presenting information objectively with facts and evidence.
- Don’t voice your personal opinions or use subjective statements.
- Strive for clarity and simplicity in your language and ensure that your message is easily understood.
- Avoid unnecessarily complexity or convolution.
- Don’t use hyperbole or excessive claims.
- Use strong verbs, active voice, and concise language to make your points effectively.
- Aim to resonate with the reader’s interests and concerns.
By striking the right balance between professionalism, clarity, and engagement, you can effectively deliver your message and compel the reader to take action or make informed decisions based on the summary.
4. Avoid cliché language.
With any style of writing, it’s best to avoid clichés. Clichés can convey the wrong message or be misunderstood, which is something you want to avoid when someone reads your executive summary.
Additionally, clichés tend to overpromise and under-deliver. For example, including something like “The Best Restaurant in Town” isn‘t true because you’re untested as a business. Your executive summary should reflect the truth and who you are as a company.
To avoid clichés while writing, it’s essential to be aware of their presence. Familiarize yourself with common clichés and be mindful of them as you write. Some examples include:
- “Thinking outside the box”
- “Innovative solutions”
- “Cutting-edge technology”
Instead of relying on these overused phrases, be descriptive and embrace the uniqueness of your brand when writing your executive summary. For instance, there’s no need to vaguely refer to your product as a “game-changer,” when you could explain how it benefits your target audience instead. Show, don’t tell.
By staying true to your voice and delivering an honest message, you can keep your writing fresh and your audience engaged.
5. Write it after completing your business plan.
An executive summary is a summary of your business plan. However, it‘s hard to write a summary when you haven’t written your business plan yet. That’s why your executive summary should be the final thing you write.
By saving this step for last, you’re able to gain a thorough understanding of the entire plan, including your business’s goals, strategies, market analysis, and financial projections. This enables you to accurately depict the most important aspects in your summary.
If you write you executive summary first, you’re more likely to miscommunicate the essence of your business plan to executives and shareholders. Sure, you may have an outline prepare, but not having all the information can lead to inconsistencies or inaccuracies in your summary. You also risk including irrelevant details or omitting important details that come up during the planning process.
Ultimately, writing your executive summary last ensures that precisely represents the content and findings your plan.
If you don’t have a business plan yet, don’t worry; we have a comprehensive business plan template to help you create one quickly and effectively.
Featured Resource: Business Plan Template
Download Your Free Template Here
Now that you know how to write an executive summary, let’s dive into the details of what to include.
What to Include in Your Executive Summary
Your business plan should convey your company‘s mission, your product, a plan for how you’ll stand out from competitors, your financial projections, your company’s short and long-term goals, your buyer persona, and your market fit.
Ultimately, an executive summary should provide a preview for investors or CEO’s, so they know what to expect from the rest of your report. Your executive summary should include:
- The name, location, and mission of your company
- A description of your company, including management, advisors, and brief history
- Your product or service, where your product fits in the market, and how your product differs from competitors in the industry
- Financial considerations, start-up funding requirements, or the purpose behind your business plan — mention what you hope the reader will help your company accomplish
How long should an executive summary be?
While there is no hard and fast rule for the exact length, executive summaries typically range from one to three pages. However, it’s important to note that the length should be determined by the document it accompanies and the content itself rather than a predetermined page count.
At the end of the day, your executive summary should engage the reader and highlight the most important points of your document while avoiding unnecessary details.
Feeling at a loss? Download a free template below that will take you through the executive summary creation process.
Executive Summary Template
Download Your Free Executive Summary Template Here
In this free executive summary template, you’ll be able to outline several pieces of information, including:
- Introduction: Explain what your executive summary contains.
- Company & Opportunity: Explain who you are and your biggest opportunities for growth.
- Industry & Market Analysis: Explain the state of your industry and your target market.
- Management & Operations: Explain who your key leaders are and their roles.
- Implementation & Marketing: Explain how you plan to deploy your product to the marketplace.
- Financial Plan: Explain your company’s finances. Change the verbiage depending on whether you’re writing to investors or a general audience.
- Conclusion: Summarize what you’ve covered.
Ready? Download your free executive summary template.
To understand more tactically how an executive summary should look, let’s review a few examples.
Executive Summary Examples
1. Connected
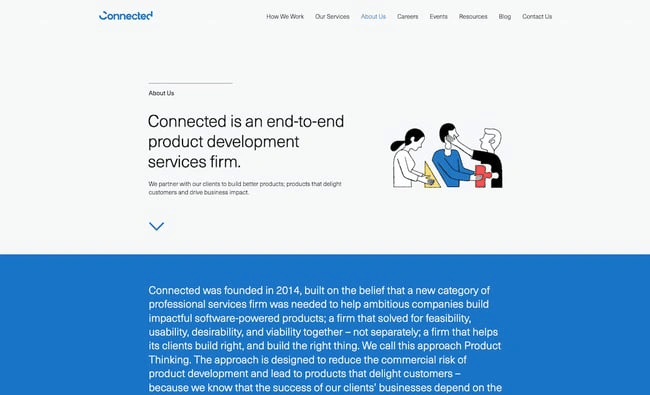
Connected’s executive summary immediately grabs your attention with its headline, which describes what the company does in a succinct, clear way. Even if you don’t read the rest of the summary, you’ll understand what Connected does from the heading alone. The company then goes into its history, mission, and values at length.
Try It Yourself
Use the heading of your page to immediately describe what you do, as opposed to using “About Us” or “Executive Summary” as the title. Give readers the opportunity to get what they need above the fold and the option to read more. Note that this would not apply in an executive summary in a business plan.
2. Events Industry Council
Events Industry Council’s executive summary is short and sweet, yet provides plenty of information for readers to understand what the organization does and which products it offers. Note the brevity in the mission, vision, and values sections — that demonstrates that there’s no need to go on at length if it doesn’t suit you. The “Who we are” section has the most emphasis here, which is a powerful technique to draw readers’ attention.
Try It Yourself
Spend more time in the section that you feel your audience will care most about. If you’re pitching to investors, you might spend more time on the Market Analysis and Financials sections. If you’re writing for a general audience, you might focus on your company background.
3. Company Shop Group
One of the first things you see when visiting Company Shop Group’s About Us page is its subheading: “Company Shop Group is the UK’s leading redistributor of surplus food and household products.” Like Connected, Company Shop Group includes what it does above the fold, so that readers have the option to either keep reading or walk away knowing what the company is about. The organization also includes multimedia to engage visitors and explain its business model in a more digestible format.
Try It Yourself
Include what you do above the fold and add multimedia elements to provide an alternative way for readers to learn more about you. Videos, images, and headings can make it much easier to scan your executive summary, but be careful to only use this method for the right audience and through the right medium. (You might not include images inside a formal business plan, for instance.)
4. FirstEnergy
FirstEnergy’s executive summary is great inspiration if you’re a more corporate, formal brand. The company’s executive summary covers its mission, subsidiaries, operations, products and services, corporate responsibility values, and strategic plan goals. This is useful information for potential investors, as the company is publicly traded.
While it’s comprehensive, the executive summary remains short, using bullet points and images to break up the information and giving readers the opportunity to explore more with a sidebar menu.
Try It Yourself
Be conscious of the status of your company when writing your executive summary. If it’s publicly traded, you’ll want to include more information, such as your strategic plan and expansion opportunities. If you’re publishing your executive summary on your website, use a sidebar to allow readers to jump from page to page without leaving their place.
Start Your Executive Summary
An executive summary should be short and concise, but it should still convey who you are as a company. If you’re starting a company, remember to tell your story, while also including important background and financial information. A strong executive summary will pave the way for more investors to invest in your business and more customers to trust in your brand.
Editor’s note: This post was originally published in December 2018 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.
This article was written by a human, but our team uses AI in our editorial process. Check out our full disclosure to learn more about how we use AI.









![How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://moz.com/images/blog/banners/BlogHeader-AI-v1.png?w=1200&h=630&q=82&auto=format&fit=clip&dm=1689270463&s=a9b702386e34d9e3246f10f15edf310a)
![How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/clickable-call-to-action-examples.png#keepProtocol)
![How to Optimize for Google’s Featured Snippets [Updated for 2024]](https://moz.com/images/blog/Blog-OG-images/How-to-Optimize-for-Googles-Featured-Snippets-OG-Image.png?w=1200&h=630&q=82&auto=format&fit=crop&dm=1724004002&s=13df73104762982790dab6dc8328023f)


