Whether you’re working with a new customer or another department at your company, one of the most critical steps for alignment is creating a service level agreement (SLA). However, you may be wondering, “what is an SLA and how do I write one?”
Traditionally, an SLA serves to define exactly what a customer will receive from a service provider. Here, we’ll explain the different types of SLAs, what they include, how to create one, and examples to draw inspiration from.
Service Level Agreement (SLA)
A service level agreement (SLA) is a contract that establishes a set of deliverables that one party has agreed to provide another. This agreement can exist between a business and its customers, or one department that delivers a recurring service to another department within that business.
Ultimately, a service level agreement is designed to create alignment between two parties by setting clear expectations and mitigating any issues before they happen. With that in mind, there are multiple types of SLA depending on your use case.
What are the 3 types of SLA?
- Customer Service Level Agreement
- Internal Service Level Agreement
- Multilevel Service Level Agreement
1. Customer Service Level Agreement
A customer SLA is just what it sounds like: an agreement by a vendor to deliver a certain level of service to a particular customer. Here’s a fun example:
In the TV show The Office, the company, Dunder Mifflin, supplies paper to various organizations. They might have a customer SLA stipulating that Dunder Mifflin will supply [Company X] with 50 reams of paper per month, shipped every Monday to [Address 1] and [Address 2] by Darryl Philbin — with a confirmation of delivery sent to Jim Halpert. (Sorry, we had a little too much fun with the references in that one.)
2. Internal Service Level Agreement
An internal SLA only concerns parties from within the company. While a business might have an SLA open with each of its clients, it can also have a separate SLA between its sales and marketing departments.
Let’s say Company X’s sales department has to close $5,000 worth of sales per month in total, and each sale is worth $100. If the sales team’s average win rate for the leads they engage with is 50%, Company X’s marketing director, Amir, can work with the sales team on an SLA, stipulating that Marketing will deliver 100 qualified leads to sales director, Kendra, by a certain date every month. This might include four weekly status reports per month, sent back to Amir by Kendra, to ensure the leads Kendra’s team is receiving are helping them keep pace with their monthly sales goal.
3. Multilevel Service Level Agreement
Multilevel SLAs can support a business’s customers or the business’s various internal departments. The point of this type of SLA is to outline what is expected of each party if there’s more than just one service provider and one end user. Here’s an example of a multi-level SLA in an internal situation:
Company X’s sales and marketing teams partner up on an internal SLA that delivers leads from Marketing to Sales every month. But what if they wanted to incorporate a customer retention strategy into this contract, making it an SLA between Sales, Marketing, and Customer Service?
After sales closes 50 new deals for the month, it’s Customer Service’s job to keep these customers happy and successful while using the product. In a multi level SLA, Company X can have sales director, Kendra, send monthly “customer friction” reports to Joan, the VP of service, based on dialogue the sales team has regularly with its clients. This helps the customer service team build a knowledge base that better prepares them for the pain points customers call them about.
You can learn more about customer service’s increasing role to business growth in the HubSpot Academy.
How to Write an SLA
- Define the scope of service.
- Specify the responsibilities of both parties.
- Set performance metrics.
- Define the reporting requirements.
- Establish the escalation process.
- Specify penalties and incentives.
- Put it all together.
A thorough and effective SLA ensures that the expectations of both parties are clearly defined and understood, leading to a successful and productive partnership. To write an SLA, you should:
1. Define the scope of service.
Defining the scope of service is an essential part of writing an SLA because it details the service that is to be received and the level of support that will be provided.
It also outlines the expected performance and quality levels, as well as the hours of operations.
The scope of service should be thorough enough to ensure that everyone involved has a shared understanding of what is being offered, how it will be delivered, and what can be expected.
2. Specify the responsibilities of both parties.
Specifying the roles of both parties helps to ensure that there is a shared understanding of the service delivery process, the points of contact, and who is responsible for what.
This helps set clear expectations and avoid misunderstandings of conflicts that might occur during the service delivery process.
3. Set performance metrics.
Performance metrics establish a baseline for measuring the success of the service provided.
They help define the objectives of the service, specify what needs to be delivered, and ultimately, ensure that the services are delivered in an efficient and effective manner.
Plus, high-quality performance metrics can demonstrate the value of the service, as well as provide a means to improve the services provided based on feedback gathered from the metrics themselves.
4. Define the reporting requirements.
In addition to setting performance metrics, you should also define reporting requirements when writing an SLA. This provides a way to track the progress of the service delivery process, ensuring that the SLA is being adhered to.
Reporting requirements outline how, when, and what information should be reported on the performance of the service delivered to the recipient.
These requirements can include regular SLA reviews, performance monitoring reports, and other metrics relevant to the success of the service delivery process.
Not only will this ensure transparency in the service delivery process, but it will also promote better communication between both parties, and identify any issues that need addressing.
5. Establish the escalation process.
When an issue occurs, having an escalation process in place outlines the steps to be taken to resolve the issue promptly and effectively.
Not only does it provide a clear path for communication between the service provider and the recipient in the event that something goes wrong, it can also help prevent delays in addressing issues, reduce the likelihood of conflict, and ensure that issues are resolved in a timely manner.
Plus, an escalation process can help to identify recurring issues in the service delivery process, providing a means of continuous improvement in the service.
6. Specify penalties and incentives.
Penalties and incentives provide a level of accountability for the service provider while also incentivizing them to provide the best quality of service to the recipient. They can be used to encourage quality service delivery, motivate effective response to incidents, and ensure the fulfillment of commitments in the SLA.
Penalties can be financial or non-financial and may include discounts, refunds, or additional services, among others, for failing to meet specific service level targets.
On the other hand, incentives, like bonuses and additional services, can be offered to motivate service providers to achieve the highest performance levels.
7. Put it all together.
Once you and the other party have considered the steps above, gather all the information you have, format it in a document, and share it with all stakeholders. Allow everyone time to read through the details and provide feedback.
After each party has agreed to the conditions of the SLA, have them sign it on a final draft and distribute.
Keep in mind that SLAs should exist as a living document. Therefore, if issues arise and the service level needs to be adjusted, the document should be revised to reflect the changes and redistributed to all stakeholders.
What does an SLA include?
The details of an SLA will differ among internal and external agreements. Nonetheless, there are common building blocks that each SLA should include, whether the recipient of the service is your customer or your sales team.
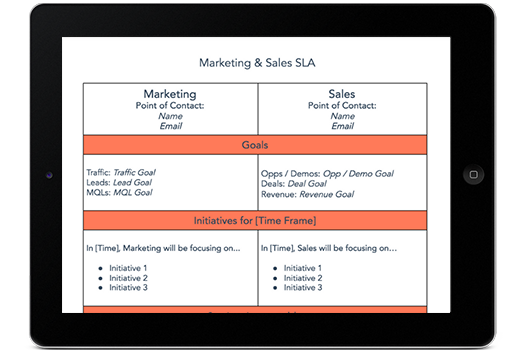
Featured Resource: Free Marketing & Sales SLA Template
 Download this Template
Download this Template
HubSpot’s Sales & Marketing SLA Template is the ideal resource for outlining your company’s goals and reaching an agreement between these two crucial teams. Download it now for free.
1. A Summary of the Agreement
The first item on your SLA should be an overview of the agreement. What service have you agreed to deliver to the other party? Summarize the service, to whom it’s being delivered, and how the success of that service will be measured.
2. The Goals of Both Parties
In external SLAs — those between a business and its customers — the goals stated in the agreement are primarily those of the customer. If this is your intention, work with your client to marry their needs with the abilities of your product, and come up with a measurable goal that your company can feasibly meet for the client on a regular basis.
Is this an internal SLA between your sales and marketing departments? Both teams should have their goals outlined in this section of the contract, while making sure that when Marketing hits its goal, Sales can reach its own goal as a result.
3. The Requirements of Both Parties
SLAs should include what each party needs in order to reach their goals. In agreements that serve a customer, keep in mind their needs might go beyond simply “the product.” They might need more than that to reach their goals — such as weekly consulting, reporting, and technical maintenance from you.
SLAs between sales and marketing teams should describe what they might need from the opposite department in order to help them hit their targets. Marketing, for example, might need weekly status reports on Sales’ pipeline so the marketers can adjust their lead-generating campaigns accordingly.
4. The Points of Contact
Who’s in charge of making sure each party’s goals are met? Sort out which team does what, and who talks to whom, in this section of your SLA. Is there a separate employee using the services, in relation to the employee who reports on performance every week? Make it clear who’s involved in the SLA, and how.
5. A Plan if Goals Aren’t Met
You might not want to think about it, but there should be formal consequences when a goal isn’t met as part of an SLA. Don’t freak out, though — these consequences aren’t always business-ending situations. Include a form of compensation to the service’s end user for when the service doesn’t meet their agreed-upon goals. In external SLAs, according to PandaDoc, this compensation can come in the form of “service credits.” Grab PandaDoc’s free SLA template here to find out more.
For Sales and Marketing SLAs, work with your sales team to establish a plan for how any lost revenue is to be made up as a result of an unreached sales quota. You might settle on a strike system that holds certain employees — in both Sales and Marketing — accountable for diagnosing and resolving issues of low performance.
6. The Conditions of Cancellation
Under what circumstances will your SLA be terminated?
Whether your contract serves a customer or two internal departments, you’ll typically find yourself putting the SLA on the chopping block when it’s just not working. Maybe your goals have gone unmet for the last three months, or the current agreement simply doesn’t have buy-in from everyone involved.
Come up with formal conditions under which you’d cancel the current SLA in pursuit of, hopefully, a better SLA.
Examples of SLAs
While an SLA will be unique to your needs, here are some examples and templates that can give you an idea of what an SLA may look like.
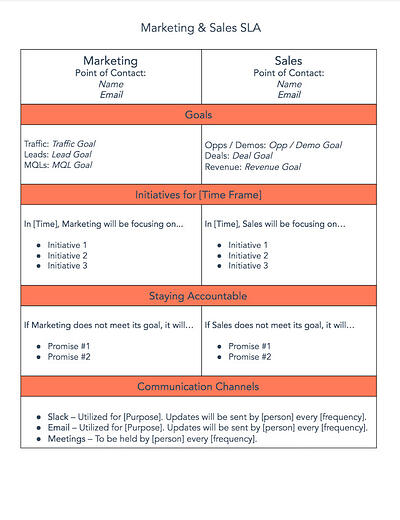
1. HubSpot’s Marketing & Sales SLA Template
As previously mentioned, HubSpot has a template for marketing and sales service level agreements. Instead of being overly complicated, the template provides straightforward, no-nonsense sections so that any party can skim at a glance.
What we like best: It’s laid out in a two-column style to easily denote which team is responsible for which activities and metrics. Having them side-by-side like this further underscores the goals of partnership and alignment.
How to Implement This in Your SLA
Simplicity is the key to recreating this SLA template. Whether you use HubSpot’s offering or create your own, effectively implementing this type of SLA means resisting the temptation to list out every possible outcome and instead focus on the big picture of goals, initiatives, and accountability.
2. Hivehouse Digital’s Marketing & Sales SLA Template
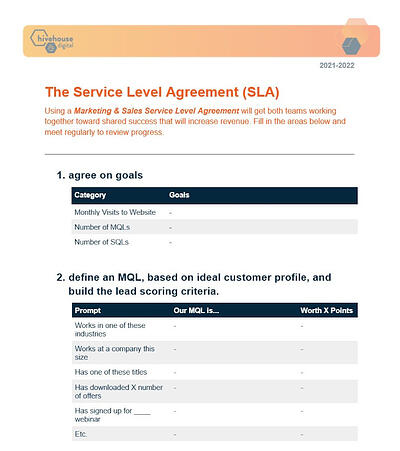
This sales and marketing SLA template focuses heavily on metrics, making it a great choice for high-performance teams. The design relies on tables for easy information input and even comes with prompts/examples to help you define the agreement.
What we like best: The document is organized step-by-step, making it a great choice for teams without a formalized SLA process (yet).
How to Implement This in Your SLA
Implementing the Hivehouse model for your SLA means leaning into its step-by-step strengths. By breaking down SLAs into smaller and more manageable steps, there’s less chance of you and your team getting overwhelmed.
3. Lucidchart’s Marketing and Sales SLA Template With Examples
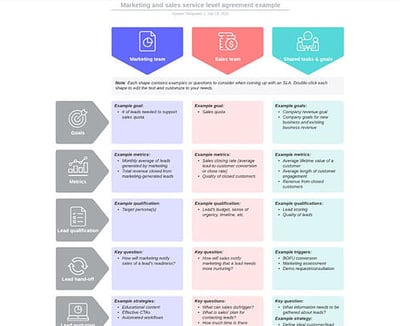
Instead of going through the process of creating an SLA, this template organizes sections by the marketing and sales process itself, from goals to lead qualification, handoff, and nurturing.
What we like best: The template takes a visual approach with columns for marketing, sales, and shared goals. This makes ownership of deliverables crystal clear throughout the process.
How to Implement This in Your SLA
Seeing is believing in this type of SLA template. While the nitty-gritty details are there, this approach uses color and shape to highlight important categories and actions. If you’re planning to take this approach to your SLA, use color psychology and graphic design principles to create a visually appealing SLA.
4. AT&T’s Small Business Service Agreement Example
Here’s a real-world example in the wild. Not all SLAs are between marketing and sales teams or even other internal departments. Here’s an SLA that lays out a service agreement between AT&T and its customers, setting expectations for the engagement. They make this SLA publicly accessible for all their users.
What we like best: The agreement is plain and simple, leveraging bullet points to make each detail clear and understandable.
How to Implement This in Your SLA
AT&T’s real-world example highlights the importance of calling out what matters — in this case, by using bullet points. Applying the same approach to your SLA means distilling larger and more complicated outcomes into easily-understood snippets that don’t leave room for confusion.

5. Microsoft SLA Example for Online Services
As a service provider, Microsoft also makes its SLA for customers public. The SLA uses bullet points to clearly identify its offerings and customer promises, which are unique depending on the plan and services rendered.
What we like best: The SLA is organized with headings for quick navigation to the offerings that are most pertinent, and information is kept concise with an optional “View full details” link.
How to Implement This in Your SLA
In-depth SLAs are naturally complicated, making it easy to get bogged down in the details despite best efforts to keep things simple. Microsoft’s example offers a streamlined approach to implementation: Call out the key details and then provide links to the full SLA text.

6. PandaDoc’s Multi-Page SLA Template
PandaDoc provides another option for provider/client agreements and is a great choice for more formal arrangements.
What we like best: This template makes for a clear and concise SLA with times, dates, and solid expectations.
How to Implement This in Your SLA
While this type of SLA leans more toward legalese with language like “whereas” and “therefore”, it has the advantage of a solid narrative structure to describe expectations. If you’re planning to implement something similar, consider using a template to speed up the process rather than starting from scratch.

How to Make an SLA for Marketing and Sales Alignment
While SLAs are common between businesses and new customers, they can also improve internal alignment. When one exists between sales and marketing departments in particular, this agreement details marketing goals (like number of leads or revenue pipeline) and the sales activities that’ll follow and support them (like engaging leads that were qualified by the marketing team).
Both the sales and marketing departments use this document as a commitment to support each other based on concrete, numerical goals. And guess what? 87% of sales and marketing leaders say collaboration between sales and marketing enables critical business growth.
Now, if you don’t have a Sales and Marketing SLA in place, fear not: We’ve outlined how to create one below so that you can easily start aligning your sales and marketing teams.
To draft your SLA, you first need to align your Sales and Marketing teams around a shared set of goals — or, as we put it before, the harmonious “Smarketing.” This alignment can then dictate the creation of a written SLA that reflects these goals. Here’s how to create an SLA with “Smarketing” in mind:
1. Calculate a numerical marketing goal based on the sales team’s quotas.
As a marketing department, not only should you have a concrete goal for each campaign you run, but you also should have a high-level numerical goal that aligns with the sales team’s operations. At the end of the day, that’ll mean qualified leads and actual sales from those leads.
Salespeople are driven almost entirely by their sales quotas — the numerical goals that correlate with their compensation and job security. If Marketing commits to a similar, related numerical goal, it shows that the team is being held accountable in a manner similar to Sales. The trick, however, is to make sure your numerical goal can effectively power the sales team’s numerical goal.
In order to calculate the marketing side of your SLA, you’ll need the following four metrics:
- Total sales goal (in terms of revenue quota)
- % revenue that comes from marketing-generated leads (as opposed to sales-generated ones)
- Average sales deal size
- Average lead-to-customer close %
Then, it’s time to do some calculations:
- Sales quota x % revenue from marketing-generated leads = Marketing-sourced revenue goal
- Marketing-sourced revenue goal ÷ Average sales deal size = # of customers needed
- Customers ÷ Average lead-to-customer close % = # of leads needed
2. Segment your goals by specific intervals during the year.
It might also be a good idea to reevaluate the marketing side of the SLA each month, as a variety of factors can change the numbers used in your calculations over time. To do so, create a document that tracks your SLA calculations by month, which should include the following metrics:
- # of marketing-generated leads
- # of those leads that became customers
- Revenue from those closed customers
- Total revenue closed that month from marketing-generated leads only
- Total revenue closed that month
You will also need:
- The average sales cycle length
With the figures above, you can re-calculate the metrics you started with on a monthly basis, or at whichever interval suits your business — quarter, year, etc. Just make sure the same measure of time is used for both Sales and Marketing to maintain alignment. Have a look:
- # marketing-generated leads that became customers ÷ # marketing-generated leads = lead-to-customer close %
- Revenue from closed customers ÷ # of marketing-generated leads that became customers = sales deal size
- Total revenue closed from marketing-generated leads / total revenue closed = % revenue from marketing-generated leads
You could also take it one step further, and incorporate quantity and quality into these metrics. The above calculations provide you with a quantitative volume goal of marketing-generated leads. However, we know that not all leads are created equal, and as a result, some may be considered higher- or lower-quality than others.
For example, a decision-making executive might be a more valuable contact than an intern. If that’s the case, you can do the above analysis for each subset of leads, and set up separate goals for each type/quality level.
Want to take it even further? Measure in terms of value, instead of volume. For example, a CEO may be worth $100, for instance, while a director is $50, a manager is $40, and so on.
3. Calculate sales’ figures and their goals.
The sales side of the SLA should detail the speed and depth to which a salesperson should follow up with marketing-generated leads. When establishing this end of the SLA, consider these two sales statistics:
- Salespeople who follow up with leads within an hour are nearly seven times more likely to have meaningful conversations with a decision maker on the other end.
- However, only 7% of leads respond to a follow-up contact within five minutes after filling out a form.
Bottom line? Not all leads may be fit to send to sales immediately. They often need to meet some minimum level of quality, like reaching a certain activity level, which can only take place after being nurtured by Marketing.
Nonetheless, engaging a lead the short time after he/she converts is critical to maintaining a relationship with them — the question you have to answer is what that engagement should look like. Either sales or marketing should take action to start building that relationship, make nurturing easier, and set up the sales rep for success when she eventually does reach out.
Keep in mind this advice is futile if you don’t consider the bandwidth of your sales reps. Sure, in a perfect world, they’d make six follow-up attempts for each lead — in reality, though, they may simply not have enough hours in the day to do that. For that reason, you’ll also need to factor in the number of leads each rep is getting (based on the marketing SLA), how much time they spend on marketing-generated leads versus sales-generated leads, and how much time they have to spend on each one. If you’re looking to conserve time, some of the follow-up — email, in particular — could be automated, so look into options there.
4. Set up marketing SLA reporting.
Now that you have your SLA goals, it’s time to track your progress against that goal — daily.
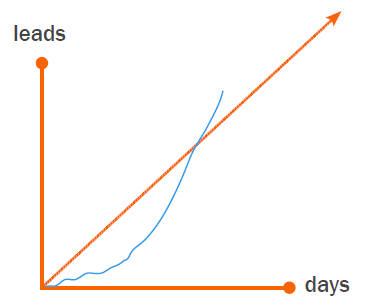
To start, graph the goal line using this formula:
(1÷n x g)
Where n is the number of days in the month and g is your monthly goal.
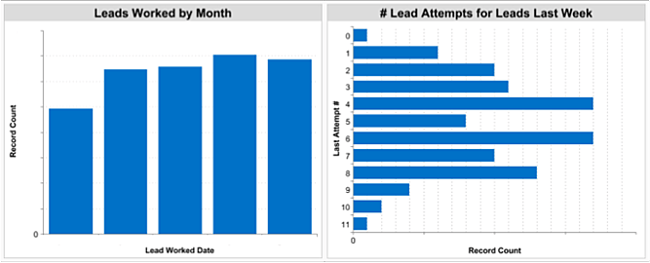
That should determine what portion of your monthly goal you need to achieve each day. You’ll want to graph that cumulatively throughout the month and mark your cumulative actual results on the same chart. We call that a waterfall graph, and it looks something like this:
5. Set up sales SLA reporting.
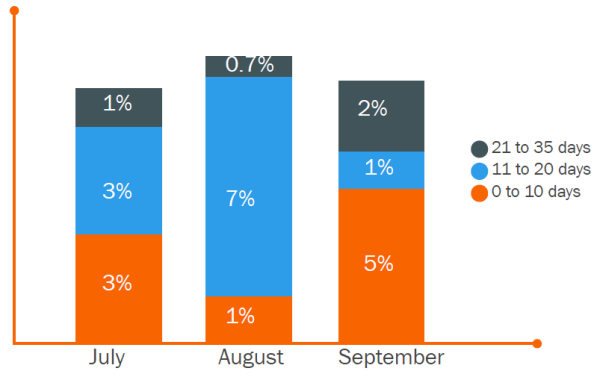
For the sales SLA reporting, you’ll have two graphs — one monitoring the speed of follow-up, and the other monitoring the depth of follow-up.
To graph the speed of follow up, you’ll need the date/time the lead was presented to sales, and the date/time the lead received her first follow-up. The difference between those two times equals the time it took for sales to follow up with that particular lead.
Take the averages of lengths of time it took for sales to follow up with all leads within a particular timeframe — day, week, month — and chart it against the SLA goal.
To graph the depth of follow-up — e.g., the number of attempts — look specifically at leads that have not been connected with, since the goal of the follow-up is to get a connection. For leads over a certain timeframe that have not received outreach, look at the average number of follow-up attempts made, and graph that against the SLA goal.
6. Communicate, celebrate, and address the achievement (or lack thereof).
Maintaining strong communication regarding how each team is performing on goals boosts transparency. If either team isn’t reaching their goals, addressing that confirms their importance, while celebrating hitting those goals can aid motivation.
If you’re not sure where to begin when it comes to setting these goals, check out our free Marketing & Sales Lead Goal Calculator, designed to help you determine and track the goals that will eventually become part of your SLA.
SLA Best Practices
- Define Realistic Goals
- Ensure Everyone is On Board
- Get Specific
- Pinpoint Key Metrics
- Account for the Unexpected
- Double-Check the Details
- Review and Revise as Needed
To ensure you’re getting the most from SLA creation, implementation and management, it’s worth aligning your efforts with industry best practices. Some of the most common include:
Define Realistic Goals
While promising the moon might seem like a good idea, things can quickly go off track when SLA outcomes aren’t met. As a result, it’s worth starting SLA creation with a brainstorming session that includes relevant stakeholders. Here, the goal is to define what you want to do, what you can do, and what you can reasonably offer.
Ensure Everyone is On Board
Next, make sure all relevant parties feel like their needs are being met with your draft SLA. Better to find out up-front that there are potential problems — and make proactive changes — than face pressure to scrap in-place service level agreements and start over.
Get Specific
Specificity is what makes SLAs work. For example, if you’re an IT service company drafting an SLA about uptime, the number of “nines” — 99.999 percent, 99.9999 percent, etc. — defines exactly how much uptime you’re agreeing to provide. Using specific terminology reduces the risk of conflict around SLA expectations by removing ambiguity.
Pinpoint Key Metrics
While specific SLAs are a solid starting point, you also need ways to effectively measure the success of your agreement. In the uptime example above, minutes of downtime per year are often used to determine if goals are being met. When it comes to marketing or sales, meanwhile, metrics could include leads generated, deals closed, or any other measurement that makes sense under your SLA structure.
Account for the Unexpected
Unexpected events — such as severe weather, staffing challenges, or sudden IT failures — can make SLA goals challenging to reach. As a result, it’s worth creating clauses that account for unexpected events. While there’s no way to predict exactly what will happen, and obligations remain to meet at least minimum standards, building in some breathing room for the unexpected is well worth the effort.
Double-Check the Details
Even small details matter. Consider the example above: While 99.999 percent uptime works out to just over 5 minutes of downtime per year, 99.9999 percent is 31 seconds. Here, a misplaced 9 could put your company on the hook for providing service levels that are almost impossible to reach. As a result, it’s worth getting your SLA double-checked by a fresh pair of eyes before moving forward.
Review and Revise as Needed
Service level agreements aren’t static documents. While they cover a set period and describe a specific set of actions, both provider and partner needs can change during that time. As a result, it’s worth building in the option for review part way through the SLA agreement period and conducting a full review when the contract is up to determine if changes are required.
One Last Step When It Comes to SLAs
When it comes to what should be in your service level agreement, there’s one final piece: Review these metrics on a regular basis to monitor your progress, and make sure both Sales and Marketing have access to the reports for both sides of the SLA.
This step helps to maintain accountability and transparency and allows for both teams to address issues — or congratulate each other on productive results.
Editor’s Note: The post was originally published in January 2019 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.






![How to Optimize for Google’s Featured Snippets [Updated for 2024]](https://moz.com/images/blog/Blog-OG-images/How-to-Optimize-for-Googles-Featured-Snippets-OG-Image.png?w=1200&h=630&q=82&auto=format&fit=crop&dm=1724004002&s=13df73104762982790dab6dc8328023f)


